1st PUC Geography Question and Answer – Natural Hazards and Disasters
Looking for 1st PUC Geography textbook answers? You can download Chapter 11: Natural Hazards and Disasters Questions and Answers PDF, Notes, and Summary here. 1st PUC Geography solutions follow the Karnataka State Board Syllabus, making it easier for students to revise and score higher in exams.
Karnataka 1st PUC Geography Textbook Answers—Reflections Chapter 11
Natural Hazards and Disasters Questions and Answers, Notes, and Summary
1st PUC Geography Chapter 11
Natural Hazards and Disasters
Scroll Down to Download Natural Hazards and Disasters PDF
I. Answer the following in a word or a sentence each
Question 1.
What is a Natural Hazard?
Answer:
A natural hazard is a threat caused by a naturally occurring event that negatively affects people or the environment.
Question 2.
What do you mean by Natural Disaster?
Answer:
A natural disaster is a major adverse event caused by natural processes of the Earth resulting in loss of life and property.
Question 3.
Mention any two types of disasters.
Answer:
Tectonic disasters and Meteorological disasters.
Question 4.
What are floods?
Answer:
Floods are high stream flows that overflow the natural banks of rivers and submerge surrounding areas.
Question 5.
Name the most important flood prone area of India.
Answer:
The Ganga basin.
Question 6.
Why are cyclones caused in the Bay of Bengal?
Answer:
Cyclones are caused due to intense heating and low-pressure conditions over the Bay of Bengal.
Question 7.
What is drought?
Answer:
Drought is a prolonged period of water shortage due to inadequate rainfall.
Question 8.
Which region of India is in the extreme drought prone area?
Answer:
Western Rajasthan.
Question 9.
Why does landslide occur?
Answer:
Landslides occur due to gravity, heavy rainfall, seismic activity, and human interference.
Question 10.
Mention the most important avalanche prone area of India.
Answer:
The Himalayan region, especially Jammu and Kashmir.
II. Answer the following in two or three sentences each
Question 1.
Name the two most important seismic zones of India.
Answer:
- Zone V and Zone IV are the two most important seismic zones of India.
- Zone V is the most severe and highly destructive zone, while Zone IV is a high damage risk zone.
Question 2.
Mention any four factors that cause floods.
Answer:
- Floods are caused by continuous heavy rainfall, cyclones, melting of ice and snow, and deforestation.
- Human activities like urbanization and occupation of flood plains also contribute to floods.
Question 3.
State two important flood prone areas of the country.
Answer:
- The Ganga basin and the Brahmaputra basin are the two major flood prone areas of India.
- These regions experience floods almost every year due to heavy monsoon rainfall.
Question 4.
Name any four factors that cause drought and famine.
Answer:
Reduction in annual rainfall, over-utilization of water resources, deforestation, and improper agricultural practices cause drought and famine.
Question 5.
Mention any four consequences of natural hazard and disasters.
Answer:
Natural disasters cause loss of human life and property, destruction of vegetation, displacement of population, and damage to agriculture and infrastructure.
III. Answer the following five sentences:
Question 1.
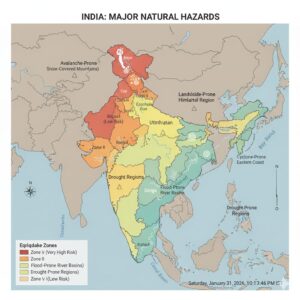
Explain the major seismic zones of India.
Answer:
Based on the intensity of earthquakes, India has been divided into five major seismic zones.
- Zone V:
This is the most severe seismic zone with an intensity above 7 on the Richter Scale. It is referred to as a Very High Damage Risk Zone. The areas include the North-Eastern states, parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Bihar, and the Kutch region of Gujarat. - Zone IV:
This zone is second in severity with an intensity between 5 and 7 on the Richter Scale. It is known as a High Damage Risk Zone. The regions include northern parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, parts of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, and West Bengal. - Zone III:
This is termed as a Moderate Damage (Very Strong) Risk Zone with an intensity between 3 and 5 on the Richter Scale. The areas include Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Maharashtra, northern Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and the western coastal region. - Zone II:
This zone is referred to as a Low Damage (Strong) Risk Zone with an intensity between 2 and 3 on the Richter Scale. The regions include Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, parts of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Odisha. - Zone I:
This zone is termed as a Very Low Damage (Slight Tremor) Risk Zone. It includes the remaining parts of India and the Deccan Plateau region.
Question 2.
Briefly explain the distribution of flood prone areas of India.
Answer:
India is highly prone to floods due to heavy monsoon rainfall and extensive river systems. The major flood prone areas are:
- a) The Ganga Basin:
The most affected states are Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal. Rivers like Ganga, Sarada, Gandak, Ghagra, Yamuna, Kosi, Bhagirathi, and Damodar frequently cause floods. Bihar experiences severe floods almost every year due to the Kosi River. - b) The Brahmaputra Basin:
The Brahmaputra River and its tributaries cause floods in Assam and North-West Bengal due to heavy rainfall. - c) The Central India and Peninsular River Basin:
In Odisha, rivers like Mahanadi, Baitarani, and Brahmani cause floods. Rivers such as Narmada, Godavari, Tapi, and Krishna cause floods in southern and central India. Cyclonic storms flood the coastal regions of Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and Tamil Nadu.
Question 3.
Explain the major drought prone areas of India.
Answer:
On the basis of the severity of droughts, India is divided into three major drought prone areas.
- a) Extreme Drought Prone Areas:
These regions experience continuous drought for many years. They include western Rajasthan, the Kutch region of Gujarat, and the arid and semi-arid regions of western and north-western India. - b) Severe Drought Prone Areas:
These areas include eastern Rajasthan, western Madhya Pradesh, parts of Maharashtra, interior Andhra Pradesh, northern and north-eastern Karnataka, and interior parts of Tamil Nadu. - c) Moderate Drought Prone Areas:
These regions are found in southern Uttar Pradesh, parts of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Tamil Nadu, and interior parts of Karnataka.
Additional Questions and Answers
I. One Mark Questions & Answers
Question 1.
What is a disaster?
Answer:
A disaster is a serious disruption caused by a natural hazard resulting in loss of life and property.
Question 2.
Name any one tectonic disaster.
Answer:
Earthquake.
Question 3.
Which seismic zone is the most dangerous in India?
Answer:
Zone V.
Question 4.
Name the scale used to measure earthquake intensity.
Answer:
Richter Scale.
Question 5.
What does Tsunami mean?
Answer:
Tsunami means “Harbour Waves”.
Question 6.
Which coast of India is most affected by Tsunamis?
Answer:
The Coromandel Coast.
Question 7.
Name one man-made cause of floods.
Answer:
Deforestation.
Question 8.
Which river causes frequent floods in Bihar?
Answer:
Kosi River.
Question 9.
Name one cyclone-prone sea of India.
Answer:
Bay of Bengal.
Question 10.
What is coastal erosion?
Answer:
Coastal erosion is the landward displacement of the shoreline caused by sea waves and currents.
II. Two Mark Questions & Answers
Question 1.
Mention any two causes of earthquakes.
Answer:
Earthquakes are caused by tectonic forces like folding and faulting, and volcanic activity.
Question 2.
State any two natural causes of floods.
Answer:
Continuous heavy rainfall and cyclones cause floods.
Question 3.
Mention any two man-made causes of floods.
Answer:
Deforestation and urbanization cause floods.
Question 4.
Name any two drought prone regions of India.
Answer:
Western Rajasthan and the Kutch region of Gujarat.
Question 5.
Mention any two effects of cyclones.
Answer:
Cyclones cause destruction of houses and loss of human life.
Question 6.
Name any two areas affected by coastal erosion in India.
Answer:
Kerala coast and Konkan coast.
Question 7.
Mention any two causes of landslides.
Answer:
Heavy rainfall and deforestation cause landslides.
Question 8.
Name any two avalanche prone states of India.
Answer:
Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh.
III. Five Mark Questions & Answers
Question 1.
Explain the causes of floods in India.
Answer:
Floods in India are caused by both natural and man-made factors.
Natural causes include continuous heavy rainfall, cyclones, melting of snow, obstruction to river flow, storm surges in coastal areas, and meandering of rivers.
Man-made causes include deforestation, unscientific agricultural practices, urbanization, disturbance of natural drainage, and encroachment of flood plains.
These factors together result in frequent floods causing loss of life and property.
Question 2.
Explain the causes and distribution of cyclones in India.
Answer:
Cyclones are caused by atmospheric disturbances around low-pressure areas, mainly over the Bay of Bengal, due to intense heating and formation of humid air masses.
They are usually accompanied by strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges.
Cyclones mainly affect the eastern coast of India, especially Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and West Bengal. The western coast experiences cyclones rarely and with less intensity.
Question 3.
Explain the causes and effects of drought and famine.
Answer:
Drought is caused by reduction in annual rainfall, excessive evaporation, overuse of water resources, deforestation, overgrazing, and improper agricultural practices.
When drought becomes severe and prolonged, it leads to famine.
The effects include scarcity of food and water, starvation, migration of population, death of livestock, and economic instability.
Question 4.
Explain the causes and distribution of landslides in India.
Answer:
Landslides are caused by heavy rainfall, seismic activity, gravity, deforestation, mining, road construction, and unscientific farming on hill slopes.
They are most common in hilly and mountainous regions.
The major landslide prone areas are Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, parts of West Bengal, and the North-Eastern states.
Question 5.
Explain the consequences of natural hazards and disasters.
Answer:
Natural hazards and disasters cause loss of human life, property, livestock, and vegetation.
They disrupt agriculture, industries, transport, communication, and public health systems.
Disasters also create fear, trauma, and psychological stress among people and affect population distribution and economic development.
