1st PUC Biology Question and Answer: Digestion And Absorption
Looking for 1st PUC Biology textbook answers? You can download Chapter 16: Digestion And Absorption Questions and Answers PDF, Notes, and Summary here. 1st PUC Biology solutions follow the Karnataka State Board Syllabus, making it easier for students to revise and score higher in exams.
Karnataka 1st PUC Biology Textbook Answers—Reflections Chapter 16
Digestion And Absorption Questions and Answers, Notes, and Summary
1st PUC Biology Chapter 16
Digestion And Absorption
Scroll Down to Download Digestion And Absorption PDF
Question and Answer:
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer among the following:
(a) Gastric juice contains
(i) pepsin, lipase and rennin
(ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin
(iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase
(iv) trypsin, pepsin and renin
(b) Succus entericus is the name given to
(i) a junction between ileum and large intestine
(ii) intestinal juice
(iii) swelling in the gut
(iv) appendix
Answers:
(a) (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin
(b) (ii) intestinal juice
Question 2.
Match column I with column II
Column I Column II
(a) Bilirubin and biliverdin (i) Parotid
(b) Hydrolysis of starch (ii) Bile
(c) Digestion of fat (iii) Lipases
(d) Salivary gland (iv) Amylases
Answer:
Column I | Column II |
(a) Bilirubin and biliverdin | (ii) Bile |
(b) Hydrolysis of starch | (iv) Amylases |
(c) Digestion of fat | (iii) Lipases |
(d) Salivary gland | (i) Parotid |
Question 3.
Answer briefly:
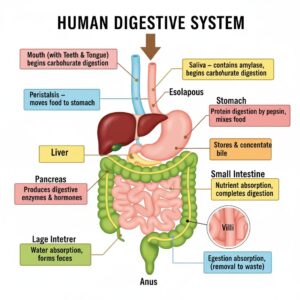
(a) Why are villi present in the intestine and not in the stomach?
Answer:
Villi are present in the intestine to increase the surface area for absorption of digested food. They contain a network of capillaries and a lymph vessel (lacteal) for nutrient transport. The stomach mainly performs digestion, not absorption; hence, villi are absent there.
(b) How does pepsinogen change into its active form?
Answer:
Pepsinogen is converted into its active form, pepsin, in the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach. Pepsin then breaks down proteins into proteoses and peptones (peptides).
(c) What are the basic layers of the wall of alimentary canal?
Answer:
The wall of the alimentary canal has four basic layers:
- Serosa – outermost thin layer of connective tissue.
- Muscularis – smooth muscle layer (inner circular and outer longitudinal).
- Submucosa – loose connective tissue with blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves.
- Mucosa – innermost layer forming villi and glands for secretion and absorption.
(d) How does bile help in the digestion of fats?
Answer:
Bile contains bile salts that help in the emulsification of fats, breaking large fat globules into small micelles. This increases the surface area for the action of lipase, which then breaks fats into di- and monoglycerides.
Question 4.
State the role of pancreatic juice in digestion of proteins.
Answer:
The pancreatic juice contains inactive enzymes trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, and procarboxypeptidases. The enzyme enterokinase, secreted by the intestinal mucosa, activates trypsinogen into trypsin, which in turn activates the other proteolytic enzymes. These enzymes digest proteins, proteoses, and peptones into small peptides and amino acids.

Question 5.
Describe the process of digestion of protein in stomach.
Answer:
The proenzyme pepsinogen present in the stomach is converted into the active proteolytic enzyme pepsin in the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl). Pepsin breaks down proteins into proteases and peptones. Rennin, another proteolytic enzyme present in the gastric juice of infants, helps in the digestion of milk proteins.
Question 6.
Give the dental formula of human beings.
Answer:
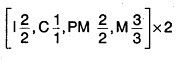
Question 7.
Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes, yet it is important for digestion. Why?
Answer:
Bile juice is a watery, greenish fluid that contains bile pigments, bile salts, cholesterol, and phospholipids but no digestive enzymes. Despite this, it plays a crucial role in digestion because it emulsifies fats, breaking large fat globules into smaller micelles, which increases the surface area for digestive enzymes (lipases) to act. It also activates lipases, making fat digestion more efficient.
Question 8.
Describe the digestive role of chymotrypsin. Which two other digestive enzymes of the same category are secreted by its source gland?
Answer:
Chymotrypsin is a proteolytic (protein-digesting) enzyme that breaks down proteins, peptones, and proteoses into dipeptides. It is secreted by the pancreas in an inactive form called chymotrypsinogen and is activated in the small intestine. The other two proteolytic enzymes secreted by the pancreas are trypsin and carboxypeptidase.
Question 9.
How are polysaccharides and disaccharides digested?
Answer:
About 30% of starch is hydrolysed by the enzyme salivary amylase into disaccharide maltose in oral cavity.

Carbohydrates in the chyme are hydrolysed by pancreatic amylase into disaccharides. Polysaccharides (starch)
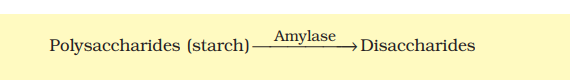
Maltase present in the intestinal juice converts maltose into glucose. Lactase converts lactose into glucose and galactose. Sucrase converts sucrose into glucose and fructose
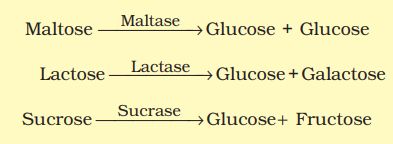
Question 10.
What would happen if HCl were not secreted in the stomach?
Answer:
HCl secreted by the stomach is important because it:
- Provides an acidic pH (around 1.8), which is optimal for the activity of pepsin.
- Converts the proenzyme pepsinogen into the active pepsin, enabling protein digestion.
- Kills harmful bacteria that may be present in food, protecting the body from infections.
Question 11.
How does butter in your food get digested and absorbed in the body?
Answer:
Butter is rich in lipids. Fat digestion begins in the stomach where gastric lipase hydrolyzes a small amount of fat. In the small intestine, bile emulsifies fats, breaking them into smaller droplets and activating pancreatic lipase, which converts fats into diglycerides, monoglycerides, fatty acids, and glycerol.
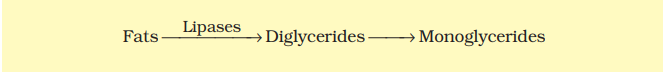
Since fatty acids and glycerol are insoluble in water, they form micelles, which are then reassembled into protein-coated fat globules called chylomicrons. These chylomicrons are absorbed by the intestinal villi and enter the lymphatic system for transport in the body.
Question 12.
Discuss the main steps in the digestion of proteins as the food passes through different parts of the alimentary canal.
Answer:
There is no protein digestion in the oral cavity as there are no proteases present.
Stomach: The proenzyme pepsinogen, on exposure to hydrochloric acid gets converted to active enzyme pepsin. Which converts proteins into proteases and peptones.
Intestine: Pancreatic juice contains inactive enzymes like trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, and procarboxy peptidases. Trypsinogen is converted to active trypsin with the help of the enzyme enterokinase. Trypsin, in turn, activates other proteolytic enzymes in the pancreatic juice. Proteins, proteoses, and peptones in the intestine are now converted to dipeptides in presence of trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase.

The aminopeptidase hydrolyses the peptide bond that attaches the terminal amino acid to the amino end of the peptide. Dipeptidase acts on dipeptides and converts them to amino acids.
Amino acids are the end products of protein digestion.
Question 13.
Explain the term thecodont and diphyodont.
Answer:
The alimentary canal begins with an anterior opening—the mouth, and opens posteriorly through the anus. The mouth leads to the buccal (oral) cavity, which contains teeth and a muscular tongue.
- Thecodont: Each tooth is embedded in a socket of the jawbone. This type of attachment is called thecodont.
- Diphyodont: Most mammals, including humans, develop two sets of teeth during their lifetime—a temporary set of milk (deciduous) teeth, replaced by a permanent set of adult teeth. This type of dentition is called diphyodont.
Question 14.
Name different types of teeth and their number in an adult human.
Answer:
An adult human has a total of 32 teeth, classified as follows:
- Incisors: 8
- Canines: 4
- Premolars: 8
- Molars: 12
Question 15.
What are the functions of liver?
Answer:
The liver is a vital organ with multiple functions, including:
- Bile Production: Produces bile, which helps in the digestion and absorption of fats.
- Detoxification: Breaks down and removes toxins, drugs, and harmful substances from the blood.
- Metabolism of Carbohydrates: Converts excess glucose into glycogen (glycogenesis) and breaks glycogen into glucose (glycogenolysis) to maintain blood sugar levels.
- Protein Metabolism: Synthesizes plasma proteins like albumin and clotting factors; converts excess amino acids into urea for excretion.
- Fat Metabolism: Converts excess carbohydrates and proteins into fats and helps in cholesterol synthesis.
- Storage: Stores vitamins (A, D, E, K, B12) and minerals (iron and copper).
- Immune Function: Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream.
Additional Questions & Answers
Question 1.
Name the enzymes present in saliva and their functions.
Answer:
Saliva contains:
- Salivary amylase (ptyalin): Converts starch into maltose.
- Lysozyme: Destroys bacteria in food.
- Mucus: Lubricates food for easy swallowing.
Question 2.
What is the role of hydrochloric acid in the stomach?
Answer:
HCl in the stomach:
- Converts pepsinogen into active pepsin.
- Provides an acidic environment for protein digestion.
- Kills most bacteria in food.
Question 3.
What is the function of bile?
Answer:
Bile:
- Emulsifies fats into smaller droplets, increasing the surface area for lipase action.
- Neutralizes acidic chyme from the stomach.
Question 4.
Name the digestive enzymes secreted by the pancreas and their functions.
Answer:
Pancreatic juice contains:
- Pancreatic amylase: Converts starch into maltose.
- Trypsin and chymotrypsin: Break proteins into peptides.
- Lipase: Converts fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Nucleases: Digest nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Question 5.
What is the role of small intestine in digestion and absorption?
Answer:
- Digestion: Enzymes like maltase, sucrase, lactase, and peptidases complete the breakdown of carbohydrates and proteins.
- Absorption: Nutrients like glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol, vitamins, and minerals are absorbed through villi into blood and lymph.
Question 6.
Give the dental formula of a human being.
Answer:
- Deciduous teeth (milk teeth):1.0.2 × 2 = 20
- Permanent teeth:1.2.3 × 2 = 32
Question 7.
Differentiate between mechanical and chemical digestion.
Answer:
Mechanical Digestion | Chemical Digestion |
Physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces | Breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules by enzymes |
e.g., Chewing in the mouth | e.g., Action of amylase, pepsin, lipase |
Does not change chemical nature | Changes chemical nature of food |
Question 8.
What is the role of large intestine in digestion?
Answer:
- Absorbs water and salts.
- Forms and stores feces.
- Houses bacteria that synthesize vitamin K and some B vitamins.
Question 9.
What are villi and their importance?
Answer:
- Finger-like projections in the small intestine.
- Increase the surface area for maximum absorption of nutrients.
- Contain blood capillaries (absorb amino acids and sugars) and lacteals (absorb fatty acids and glycerol).
Question 10.
Define: Thecodont, Diphyodont, and Heterodont.
Answer:
- Thecodont: Teeth embedded in sockets of the jawbone.
- Diphyodont: Two sets of teeth in a lifetime (milk and permanent teeth).
