2nd PUC Biology Question and Answer: Biotechnology and Its Application
Looking for 2nd PUC Biology textbook answers? You can download Chapter 12: Biotechnology and Its Application Questions and Answers PDF, Notes, and Summary here. 2nd PUC Biology solutions follow the Karnataka State Board Syllabus, making it easier for students to revise and score higher in exams.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Textbook Answers—Reflections Chapter 12
Biotechnology and Its Application Questions and Answers, Notes, and Summary
2nd PUC Biology Chapter 12
Biotechnology and Its Application
Scroll Down to Download Biotechnology and Its Application PDF
Question and Answer:
Question 1.
Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because
- bacteria are resistant to the toxin
- toxin is immature;
- toxin is inactive;
- bacteria encloses toxin in a special sac.
Answer:
(c) toxin is inactive
Explanation:
Bt toxin produced by Bacillus thuringiensis is present in the form of inactive protoxins.
These protoxins become active only inside the alkaline gut of insects, where they get solubilized and converted into active toxins.
Since the toxin remains inactive inside the bacteria, it does not harm the bacteria itself.
Question 2.
What are transgenic bacteria? Illustrate using any one example.
Answer:
Transgenic bacteria are genetically modified bacteria that carry and express foreign genes introduced into them through recombinant DNA technology.
Example:
E. coli has been made transgenic to produce human insulin.
Scientists introduced two separate DNA sequences coding for the A-chain and B-chain of human insulin into plasmids of E. coli.
These transgenic bacteria then produced the insulin chains, which were later combined to form functional human insulin used for treating diabetes.
Question 3.
Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Answer:
Advantages of GM crops:
- Genetic modification makes crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses such as cold, drought, heat, and salinity.
- Viral resistance can be introduced into plants.
- Post-harvest losses and over-ripening can be reduced.
Example: Flavr Savr tomato. - Nutritional quality of food can be enhanced.
Example: Golden rice enriched with Vitamin A. - Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides, as some GM crops (e.g., Bt crops) are pest-resistant.
Disadvantages of GM crops:
- Transgenes may escape into wild relatives, affecting native species and ecosystem balance.
- Bt toxin expressed in pollen may potentially harm non-target pollinators like honeybees.
- Weeds may develop resistance, leading to “superweeds.”
- Products of transgenes may sometimes cause allergic reactions or may be toxic to some individuals.
- Large-scale use of GM crops may cause ecological disturbances and loss of biodiversity.
Question 4.
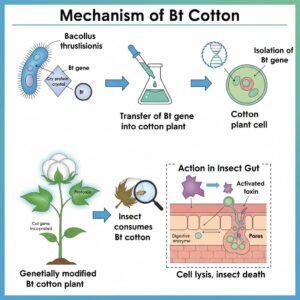
What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that produce it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Answer:
Cry proteins are insecticidal proteins (Bt toxins) that kill lepidopteran insects and their larvae. These proteins are produced by the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis.
Exploitation by humans:
The cry gene that encodes the Bt toxin has been isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis and introduced into the cotton plant genome using Agrobacterium Ti plasmid (T-DNA) as a vector.
The resulting GM crop, Bt cotton, produces the toxin in its tissues and becomes naturally resistant to insect pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Question 5
What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Answer:
- Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allow the correction of a diagnosed gene defect in a child or embryo. In this technique, normal functional genes are inserted into a person’s cells or tissues to treat a hereditary disorder.
Gene therapy is currently being tried for conditions like sickle cell anaemia and Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency (SCID). - In some children, ADA (Adenosine Deaminase) deficiency can be treated by bone marrow transplantation. In others, enzyme replacement therapy is used, where functional ADA enzyme is injected into the patient. However, neither approach gives a complete or permanent cure.
- In gene therapy, lymphocytes are taken from the patient’s blood and grown in culture outside the body.
A functional ADA cDNA is then introduced into these lymphocytes using a retroviral vector.
The genetically corrected lymphocytes are then returned to the patient, restoring partial immune function. - Because these lymphocytes have a limited lifespan, the patient requires periodic infusion of such engineered cells. A permanent cure is possible only if the functional ADA gene is introduced into early embryonic cells or bone marrow stem cells.
Question 6.
Digrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing an human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into a bacterium like E. coli?
Answer:
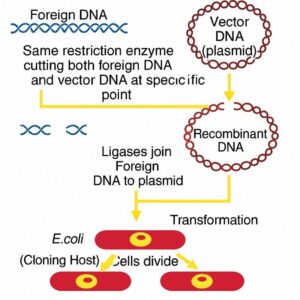
Question 7.
Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
Answer:
Yes — using rDNA tools we can reduce or eliminate oil (triacylglycerol, TAG) accumulation in seeds by manipulating seed-specific genes of the oil-biosynthesis pathway (for example, downregulating DGAT or other TAG-synthesis enzymes using RNAi or CRISPR) and/or redirecting carbon flux to starch or protein. However, this is difficult because oils are major seed energy reserves and structural oil-body proteins (e.g., oleosin) are important for seed viability. To avoid whole-plant harm, modifications must use seed-specific promoters and extensive testing for germination, agronomic performance and unintended effects.
Question 8.
Find out from internet what is golden rice.
Answer:
Golden Rice is a genetically modified (transgenic) variety of rice that has been engineered to produce β-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, in its edible part (endosperm). It contains genes responsible for vitamin A biosynthesis, which are normally absent in regular rice grains.
Golden Rice was developed by scientists at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH), Zurich, in collaboration with the University of Freiburg.
The grains appear golden yellow due to the presence of β-carotene, which is responsible for vitamin A activity.
Golden Rice was created to help combat vitamin A deficiency, a major health problem in many developing countries.
Question 9.
Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
Answer:
Yes, our blood does contain proteases and nucleases—but they are present in controlled and inactive forms, so they do not damage blood cells.
- Proteases like thrombin, plasmin, and complement proteases are present in blood.
They remain inactive until needed (e.g., for clotting or destroying pathogens). - Nucleases such as DNase and RNase are also present.
They help remove foreign DNA/RNA and clean up dead cells.
These enzymes do not degrade blood cells because they are:
- Present in inactive (zymogen) form, or
- Highly regulated by inhibitors in blood.
Question 10.
Consult internet and find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Answer:
Protein drugs cannot normally be taken orally because they get degraded by proteases and the acidic pH of the alimentary canal. To make a protein pharmaceutical orally active, it needs to be protected by a special coating or encapsulation that is resistant to digestive enzymes and stomach acid.
The major problem is that these proteins are easily broken down during digestion, so very little of the active drug is absorbed into the bloodstream.
Additional One Mark Questions
Question 1.
What is biolistic in plant genetic engineering?
Answer:
Biolistic is a method of gene transfer where DNA-coated metal particles are bombarded into plant cells using a gene gun.
Question 2.
Name the first recombinant DNA product approved for human use.
Answer:
Recombinant human insulin.
Question 3.
What are Cry genes?
Answer:
Cry genes are genes from Bacillus thuringiensis that code for insecticidal crystal proteins.
Question 4.
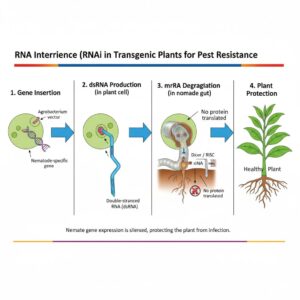
Name the nematode that infects tobacco plants and is controlled by RNAi.
Answer:
Meloidogyne incognita.
Question 5.What is pharming?
Answer:
Production of pharmaceutical proteins using transgenic animals or plants.
Additional Two Marks Questions
Question 1.
What is molecular farming?
Answer:
Molecular farming refers to the production of valuable pharmaceutical and therapeutic products (like vaccines, antibodies, hormones) in transgenic plants or animals.
Question 2.
Give any two disadvantages of genetically modified crops.
Answer:
- Risk of allergenicity due to new proteins expressed.
- GM crops may affect biodiversity by outcrossing with wild relatives.
Question 3.How does RNAi help in developing pest-resistant plants?
Answer:
RNAi silences the expression of specific pest genes by producing double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). When pests ingest these dsRNA molecules, their essential genes are blocked, resulting in death or reduced feeding.
Question 4.
What is gene therapy? Mention one example.
Answer:
Gene therapy is the correction of defective genes in patients by introducing functional genes.
Example: Treating ADA (Adenosine Deaminase) deficiency using gene therapy.
Additional Three Marks Questions
Question 1.
Explain any three ethical issues related to biotechnology.
Answer:
- Biopiracy: Exploiting biological resources or traditional knowledge without consent.
- GM food safety: Concerns about allergenicity or long-term health effects.
- Animal ethics: Genetic modification of animals raises welfare concerns
Question 2.
Describe the role of biotechnology in waste management.
Answer:
- Microbes are used to degrade organic waste in sewage treatment plants.
- Genetically engineered microbes help break down oil spills and toxic chemicals.
- Bioreactors use microbial activity to convert waste into biogas or biofertilizers.
Question 3.
Write a note on “Bt toxin mechanism of action.”
Answer:
- Bt toxin is ingested by insect larvae.
- Alkaline gut pH activates the protoxin.
- Activated toxin binds to gut epithelial receptors, forming pores.
- This leads to cell lysis and death of the insect.
Question 4.
What are the advantages of transgenic animals?
Answer:
- They produce pharmaceuticals like human proteins in milk.
- They serve as models for studying human diseases.
- They help improve livestock productivity and disease resistance.
Additional Five Marks Questions
Question 1.
Explain in detail the steps involved in the biotechnological production of vaccines.
Answer:
- Identification of antigenic gene from pathogen.
- Cloning of antigen gene into vectors.
- Expression of gene in host cells (bacteria, yeast).
- Purification of protein antigen.
- Formulation with adjuvants to create vaccine.
- Testing for safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity.
This method is used to produce vaccines like Hepatitis B vaccine.
Question 2.
Discuss bioremediation with examples.
Answer:
Bioremediation uses organisms to clean polluted environments.
Examples:
- Pseudomonas species degrade oil spills.
- Methanogens treat sewage by decomposing organic matter.
- GM plants (phytoremediation) absorb heavy metals like arsenic and lead.
This method is eco-friendly and cost-effective.
Click Here to Downlaod Biotechnology and Its Application PDF Notes