1st PUC History Question and Answer – CONTEMPORARY WORLD
Looking for 1st PUC History textbook answers? You can download Chapter 11: CONTEMPORARY WORLD Questions and Answers PDF, Notes, and Summary here. 1st PUC History solutions follow the Karnataka State Board Syllabus, making it easier for students to revise and score higher in exams.
Karnataka 1st PUC History Textbook Answers—Reflections Chapter 11
CONTEMPORARY WORLD Questions and Answers, Notes, and Summary
1st PUC History Chapter 11
CONTEMPORARY WORLD
Scroll Down to Download CONTEMPORARY WORLD PDF
I. Answer in one word or sentence each.
Question 1.
When was the term ‘Cold War’ used for the first time?
Answer:
The term ‘Cold War’ was used for the first time in 1945.
Question 2.
What is Cold War?
Answer:
Cold War was a state of political and military tension between U.S.A and U.S.S.R without direct armed conflict.
Question 3.
Who wrote an essay ‘You and the Atomic Bomb’?
Answer:
George Orwell wrote the essay ‘You and the Atomic Bomb’.
Question 4.
Name the American statesman to use the term ‘Cold War’ specifically.
Answer:
The American statesman Bernard Baruch specifically used the term ‘Cold War’.
Question 5.
Who was Truman?
Answer:
Truman was the President of the United States of America.
Question 6.
What was the aim of Marshall Plan?
Answer:
The aim of the Marshall Plan was to provide aid for the recovery and reconstruction of war-torn European countries and to contain communism.
Question 7.
In response to Marshall Plan which plan was introduced by Soviet Union?
Answer:
In response to the Marshall Plan, the Soviet Union introduced the Molotov Plan.
Question 8.
Expand NATO.
Answer:
NATO stands for North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
Question 9.
Expand SEATO.
Answer:
SEATO stands for South East Asia Treaty Organization.
Question 10.
Expand CENTO.
Answer:
CENTO stands for Central Treaty Organization.
Question 11.
When did U.S.S.R form the Warsaw Pact?
Answer:
The U.S.S.R formed the Warsaw Pact in 1955.
Question 12.
In which year was the Berlin Wall constructed?
Answer:
The Berlin Wall was constructed in 1961.
Question 13.
Name the Russian Intelligence Agency.
Answer:
The Russian Intelligence Agency was KGB (Komitet Gosudarstvennoj Bezopasnosti).
Question 14.
Name the American Intelligence Agency.
Answer:
The American Intelligence Agency was CIA (Central Intelligence Agency).
Question 15.
When was Nuclear Test Ban Treaty signed?
Answer:
The Nuclear Test Ban Treaty was signed in 1963.
Question 16.
When did Vietnam War come to an end?
Answer:
The Vietnam War came to an end in 1975.
Question 17.
Expand SALT.
Answer:
SALT stands for Strategic Arms Limitation Talks.
Question 18.
In which year did the ‘Cold War’ end?
Answer:
The Cold War ended in 1991.
Question 19.
Where is the headquarters of NATO?
Answer:
The headquarters of NATO is in Paris (later shifted to Brussels, Belgium).
Question 20.
What was the main aim of SEATO?
Answer:
The main aim of SEATO was to prevent communist aggression in South-East Asia and the Pacific region.
Question 21.
When did Soviet Union disintegrate?
Answer:
The Soviet Union disintegrated in 1991.
Question 22.
What is ‘Glasnost’?
Answer:
‘Glasnost’ was the policy of openness introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union.
Question 23.
What is ‘Perestroika’?
Answer:
‘Perestroika’ was the policy of reconstruction introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union.
Question 24.
Who headed C.I.S. after the disintegration of Soviet Union?
Answer:
Boris Yeltsin headed the Commonwealth of Independent States (C.I.S.) after the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
Question 25.
Where is the headquarters of C.I.S.?
Answer:
The headquarters of C.I.S. is at Minsk (Belarus).
II. Answer in two words or two sentence each.
Question 1.
Name any four member countries of NATO.
Answer:
U.S.A, U.K, France, and Canada were four member countries of NATO.
Question 2.
Name any four member countries of SEATO.
Answer:
U.S.A, U.K, France, and Pakistan were member countries of SEATO.
Question 3.
Name any four member countries of CENTO.
Answer:
U.K, Iran, Iraq, and Pakistan were member countries of CENTO.
Question 4.
Name the anti-American military organization. When did it come into existence?
Answer:
The anti-American military organization was the Warsaw Pact. It came into existence in 1955.
Question 5.
Name any two member countries of Warsaw Pact.
Answer:
U.S.S.R and Poland were member countries of the Warsaw Pact.
Question 6.
Name any two Independent Baltic states.
Answer:
Lithuania and Latvia are independent Baltic states.
Question 7.
Name the Presidents of America and Russia who ended the Cold War.
Answer:
Ronald Reagan was the U.S. President and Mikhail Gorbachev was the Soviet leader who ended the Cold War.
Question 8.
When was NATO established and Where?
Answer:
NATO was established in 1949 at Washington D.C.
Question 9.
Who were the human rights activists of Russia?
Answer:
Andrei Sakharov and Alexander Solzhenitsyn were the human rights activists of Russia.
III. Answer in about 15-20 sentences each.
Question 1.
Explain the causes for Cold War.
Answer:
The Cold War was the result of ideological, political, and economic differences between the U.S.A and U.S.S.R after World War II. The Soviet Union followed communism, while America supported capitalism and democracy. Both wanted to expand their respective ideologies across the world. The U.S.A introduced the Truman Doctrine (1947) to stop the spread of communism. In response, the Soviet Union expanded its influence in Eastern Europe. America launched the Marshall Plan to provide financial aid to Western European nations, while the Soviet Union created the Molotov Plan.
Formation of military alliances such as NATO (1949) by the U.S.A and the Warsaw Pact (1955) by U.S.S.R deepened the division. The Berlin Blockade (1948–49) increased tensions. The arms race and nuclear weapons competition added to the rivalry. Both nations engaged in space race and military competition. Regional wars like the Korean War and Vietnam War also reflected Cold War conflicts. Mutual suspicion and propaganda increased hostility. Thus, differences in ideology, politics, economy, and military competition caused the Cold War.
Question 2.
Write a note on Berlin Blockade.
Answer:
After World War II, Germany was divided into four zones controlled by U.S.A, U.K, France, and U.S.S.R. Berlin, though inside Soviet-controlled East Germany, was also divided into four sectors. In 1948, U.S.A, U.K, and France decided to unite their zones and introduce a new currency. The Soviet Union opposed this and started the Berlin Blockade in June 1948. All road, rail, and canal routes to West Berlin were blocked. The aim was to force the Western powers to withdraw from Berlin.
In response, the Western allies organized the Berlin Airlift (1948–49). Food, coal, and essential supplies were airlifted to the people of West Berlin. Over 200,000 flights supplied 2.3 million tons of goods. The blockade continued for almost a year but failed. Finally, the Soviet Union lifted the blockade in May 1949. This incident symbolized the beginning of the Cold War. It also led to the formal division of Germany into West Germany (FRG) and East Germany (GDR).
Question 3.
Write a note on Second Berlin crisis.
Answer:
The Second Berlin Crisis began in 1958 when Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev demanded the withdrawal of Western powers from West Berlin. He gave an ultimatum to U.S.A, U.K, and France to vacate Berlin within six months. His aim was to make Berlin a “free city” and to stop East Germans from escaping to the West. However, the Western powers refused to withdraw. The issue created high tension between U.S.A and U.S.S.R. In 1961, the Soviet-backed East German government began constructing the Berlin Wall.
The Wall physically separated East Berlin from West Berlin. It became the symbol of division between the communist East and democratic West. Families were divided and East Germans were prevented from fleeing to the West. American and Soviet tanks faced each other at Checkpoint Charlie, heightening the crisis. The Berlin Wall remained until 1989, when it was finally demolished. Thus, the Second Berlin Crisis showed the peak of Cold War rivalry in Europe.
Question 4.
Write a note on SEATO and Warsaw Pact.
Answer:
The Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) was formed in 1954 after the Indo-China war. It included countries like U.S.A, U.K, France, Pakistan, Thailand, Philippines, Australia, and New Zealand. Its aim was to prevent the spread of communism in Southeast Asia. It was often called the “Asian NATO.” However, it was criticized for being dominated by Western powers. On the other hand, the Warsaw Pact was formed in 1955 by the Soviet Union and its East European allies like Poland, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria.
It was a military alliance to counter NATO. Members promised mutual defense against any Western attack. Warsaw Pact ensured Soviet control over Eastern Europe. Both SEATO and Warsaw Pact symbolized the military division of the world during the Cold War. While SEATO declined and was dissolved in 1977, the Warsaw Pact lasted until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.
Question 5.
What were the effects of Cold War?
Answer:
The Cold War had a profound impact on world politics. Firstly, it divided the world into two power blocs – capitalist bloc led by U.S.A and communist bloc led by U.S.S.R. Secondly, it resulted in the formation of military alliances like NATO, SEATO, CENTO, and Warsaw Pact. Thirdly, it led to the arms race and the development of nuclear weapons. Fourthly, it encouraged the space race between the superpowers. Fifthly, it caused regional wars like the Korean War, Vietnam War, and Afghan War. Sixthly, the world saw the rise of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), which sought to stay out of both blocs.
Economically, America helped Western Europe through the Marshall Plan, while the Soviet Union controlled Eastern Europe. Politically, Germany and Berlin remained divided for decades. Socially, propaganda and suspicion created hostility between nations. The Cold War also led to espionage activities through CIA and KGB. Finally, it ended with the disintegration of U.S.S.R in 1991, leaving America as the sole superpower.
Question 6.
What are the factors responsible for the disintegration of Russia?
Answer:
The disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991 was caused by several factors. Firstly, the Soviet economy was weak due to excessive military spending and inefficiency. Secondly, the people suffered shortages of food, consumer goods, and basic necessities. Thirdly, political corruption and lack of democracy created unrest. Fourthly, Soviet involvement in the Afghan War (1979–89) weakened its power. Fifthly, the policies of Mikhail Gorbachev like Glasnost (openness) and Perestroika (restructuring) encouraged freedom of speech and economic reforms but also weakened central control.
Sixthly, nationalist movements arose in Baltic states like Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. Seventhly, Eastern European countries broke away from Soviet domination in 1989. Eighthly, the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 symbolized the collapse of communism. Ninthly, people demanded democracy and better living conditions. Finally, in December 1991, the Soviet Union formally disintegrated into 15 independent republics, and the C.I.S (Commonwealth of Independent States) was formed under Boris Yeltsin.
Question 7.
What are the aims and objectives of C.I.S?
Answer:
The Commonwealth of Independent States (C.I.S.) was formed in 1991 after the disintegration of the Soviet Union. Its headquarters is at Minsk (Belarus). The main aim was to maintain cooperation among the former Soviet republics. It sought to promote economic, political, and cultural ties. One of its objectives was to ensure peaceful settlement of disputes among member states. It also aimed at mutual defense and security cooperation. CIS worked for joint control over nuclear weapons after the breakup of U.S.S.R.
It promoted free trade and economic collaboration. It also aimed at respecting sovereignty and independence of member states. The CIS members agreed to cooperate in transport, communication, and environment protection. It functioned as a loose association rather than a strong federation. Though not as powerful as the Soviet Union, it provided a platform for cooperation. Hence, CIS played an important role in managing post-Soviet relations.

IV. Answer in 30-40 sentences each :
Question 1.
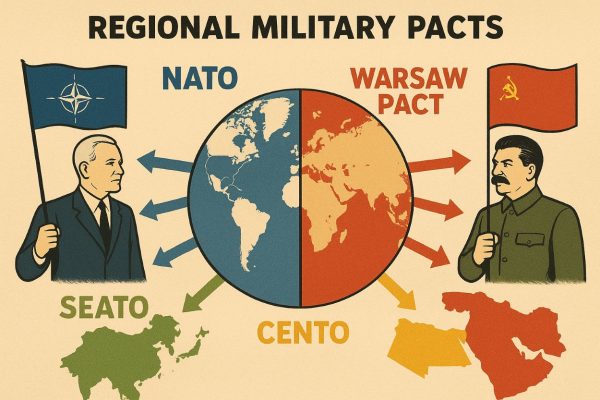
Explain Regional Military Pacts.
Answer:
- After the Second World War, the world was divided into two blocs – the American bloc and the Soviet bloc. To strengthen their influence, both powers formed a number of regional mi litary pacts during the Cold War.
- The U.S.A. and Western European nations formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 1949. Its principle was that an attack on one member would be treated as an attack on all. The main aim was to check Soviet expansion in Europe. Its members included the U.S.A., U.K., France, Canada, and Italy.
- In Asia, the South East Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) was established in 1954 with members such as the U.S.A., U.K., France, Australia, New Zealand, Pakistan, Thailand, and the Philippines. Its goal was to stop the spread of communism in South-East Asia.
- In the Middle East, the Central Treaty Organization (CENTO) was formed in 1955. It was also called the Baghdad Pact. Members included Iran, Iraq, Pakistan, Turkey, and the U.K., with U.S.A. support. Its aim was to prevent Soviet influence in the Middle East.
- In response, the Soviet Union created the Warsaw Pact in 1955 after West Germany joined NATO. Its members were the U.S.S.R., Poland, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Albania. It was meant to counter NATO and strengthen communist unity in Eastern Europe.
- These pacts divided the world into two armed camps and extended Cold War rivalry across Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. They fueled the arms race, created tensions, and turned regional issues into global conflicts.
- In conclusion, NATO, SEATO, CENTO, and the Warsaw Pact were the main regional military pacts. Instead of ensuring peace, they intensified the Cold War and prolonged international tensions until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.